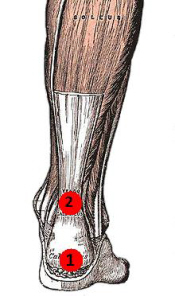
Overview

Most people have a gap under the arch of their foot when they are in a standing position. The arch, the inner part of the foot is slightly raised off the ground. People with flat feet or fallen arches either have no arch, or it is very low. The feet of people with flat feet may roll over to the inner side when they are standing or walking, and the feet may point outwards as a result.
Causes
Fallen arches in adults are caused by several things. Below are some of the most common causes. Abnormalities present from birth. Torn or stretched tendons (resulting from foot injuries or foot strains). Inflammation or damage of the PTT (posterior tibial tendon). The PTT is responsible for connecting the middle of the arch to the ankle and lower leg. Dislocated or broken bones (also as a result of injury). Health problems like rheumatoid arthritis. Nerve problems. Other factors like diabetes, obesity, aging and pregnancy (these factors are known to increase the risk of fallen arches).
Symptoms
Flat feet can cause a myriad of symptoms, from experiencing pain in the foot, heels, arch, calves, the shin, the knee, the hip and into the lower back due to overworking of the hip flexors or they may find it hard to stand on tip toes.
Diagnosis
Flat feet are easy to identify while standing or walking. When someone with flat feet stands, their inner foot or arch flattens and their foot may roll over to the inner side. This is known as overpronation. To see whether your foot overpronates, stand on tiptoes or push your big toe back as far as possible. If the arch of your foot doesn't appear, your foot is likely to overpronate when you walk or run. It can be difficult to tell whether a child has flat feet because their arches may not fully develop until they're 10 years of age.
fallen arches exercises
Non Surgical Treatment
If you have fallen arches, but you are not experiencing any symptoms, then you probably do not need to seek treatment. If you are experiencing discomfort due to fallen arches, there are several treatment options. These treatment options include elevating the feet and applying ice to ease discomfort and reduce swelling, rest, exercises to stretch the feet, physical therapy, medication, such as anti-inflammatories, steroid injections and orthotic devices or customised arch supportsto wear in the shoes. If you have fallen arches and periodically experience pain related to that condition, it is a good idea to get orthotic devicesor custom arch supports, to wear in your shoes. The other treatment options, like medication and ice, will help to ease pain from fallen arches after you have already begun to experience pain. However, orthotic devices or(custom arch supports)can help to prevent pain from occurring at all. This preventative measure helps many people with fallen arches to avoid pain and prevent worsening of their condition. In severe cases of fallen arches, surgery may be required to correct the problem. You can also help to prevent pain and exacerbation of fallen arches by reducing your risk factors. If you are overweight, try to lose weight. Even a small weight loss can reduce the pressure on your feet significantly. If you are diabetic, manage your blood sugar as best as possible. Losing weight often also improves the condition of diabetics. You should also avoid high-impact activities, like running on the road, tennis, and sports that involve jumping. Try a gentler form of exercise, like swimming, instead. If you have fallen arches, orthotic devices or(custom arch supports)are an important component of your treatment and can help to prevent pain.
Surgical Treatment

In cases of flat feet that have progressed substantially or have failed to improve with non-surgical treatment, surgery may be required and in some advanced cases, surgery may be the only option. Your foot and ankle surgeon will determine the best approach for you.
After Care
Patients may go home the day of surgery or they may require an overnight hospital stay. The leg will be placed in a splint or cast and should be kept elevated for the first two weeks. At that point, sutures are removed. A new cast or a removable boot is then placed. It is important that patients do not put any weight on the corrected foot for six to eight weeks following the operation. Patients may begin bearing weight at eight weeks and usually progress to full weightbearing by 10 to 12 weeks. For some patients, weightbearing requires additional time. After 12 weeks, patients commonly can transition to wearing a shoe. Inserts and ankle braces are often used. Physical therapy may be recommended. There are complications that relate to surgery in general. These include the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots. Complications following flatfoot surgery may include wound breakdown or nonunion (incomplete healing of the bones). These complications often can be prevented with proper wound care and rehabilitation. Occasionally, patients may notice some discomfort due to prominent hardware. Removal of hardware can be done at a later time if this is an issue. The overall complication rates for flatfoot surgery are low.
Most people have a gap under the arch of their foot when they are in a standing position. The arch, the inner part of the foot is slightly raised off the ground. People with flat feet or fallen arches either have no arch, or it is very low. The feet of people with flat feet may roll over to the inner side when they are standing or walking, and the feet may point outwards as a result.
Causes
Fallen arches in adults are caused by several things. Below are some of the most common causes. Abnormalities present from birth. Torn or stretched tendons (resulting from foot injuries or foot strains). Inflammation or damage of the PTT (posterior tibial tendon). The PTT is responsible for connecting the middle of the arch to the ankle and lower leg. Dislocated or broken bones (also as a result of injury). Health problems like rheumatoid arthritis. Nerve problems. Other factors like diabetes, obesity, aging and pregnancy (these factors are known to increase the risk of fallen arches).
Symptoms
Flat feet can cause a myriad of symptoms, from experiencing pain in the foot, heels, arch, calves, the shin, the knee, the hip and into the lower back due to overworking of the hip flexors or they may find it hard to stand on tip toes.
Diagnosis
Flat feet are easy to identify while standing or walking. When someone with flat feet stands, their inner foot or arch flattens and their foot may roll over to the inner side. This is known as overpronation. To see whether your foot overpronates, stand on tiptoes or push your big toe back as far as possible. If the arch of your foot doesn't appear, your foot is likely to overpronate when you walk or run. It can be difficult to tell whether a child has flat feet because their arches may not fully develop until they're 10 years of age.
fallen arches exercises
Non Surgical Treatment
If you have fallen arches, but you are not experiencing any symptoms, then you probably do not need to seek treatment. If you are experiencing discomfort due to fallen arches, there are several treatment options. These treatment options include elevating the feet and applying ice to ease discomfort and reduce swelling, rest, exercises to stretch the feet, physical therapy, medication, such as anti-inflammatories, steroid injections and orthotic devices or customised arch supportsto wear in the shoes. If you have fallen arches and periodically experience pain related to that condition, it is a good idea to get orthotic devicesor custom arch supports, to wear in your shoes. The other treatment options, like medication and ice, will help to ease pain from fallen arches after you have already begun to experience pain. However, orthotic devices or(custom arch supports)can help to prevent pain from occurring at all. This preventative measure helps many people with fallen arches to avoid pain and prevent worsening of their condition. In severe cases of fallen arches, surgery may be required to correct the problem. You can also help to prevent pain and exacerbation of fallen arches by reducing your risk factors. If you are overweight, try to lose weight. Even a small weight loss can reduce the pressure on your feet significantly. If you are diabetic, manage your blood sugar as best as possible. Losing weight often also improves the condition of diabetics. You should also avoid high-impact activities, like running on the road, tennis, and sports that involve jumping. Try a gentler form of exercise, like swimming, instead. If you have fallen arches, orthotic devices or(custom arch supports)are an important component of your treatment and can help to prevent pain.
Surgical Treatment

In cases of flat feet that have progressed substantially or have failed to improve with non-surgical treatment, surgery may be required and in some advanced cases, surgery may be the only option. Your foot and ankle surgeon will determine the best approach for you.
After Care
Patients may go home the day of surgery or they may require an overnight hospital stay. The leg will be placed in a splint or cast and should be kept elevated for the first two weeks. At that point, sutures are removed. A new cast or a removable boot is then placed. It is important that patients do not put any weight on the corrected foot for six to eight weeks following the operation. Patients may begin bearing weight at eight weeks and usually progress to full weightbearing by 10 to 12 weeks. For some patients, weightbearing requires additional time. After 12 weeks, patients commonly can transition to wearing a shoe. Inserts and ankle braces are often used. Physical therapy may be recommended. There are complications that relate to surgery in general. These include the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots. Complications following flatfoot surgery may include wound breakdown or nonunion (incomplete healing of the bones). These complications often can be prevented with proper wound care and rehabilitation. Occasionally, patients may notice some discomfort due to prominent hardware. Removal of hardware can be done at a later time if this is an issue. The overall complication rates for flatfoot surgery are low.

 Morton's neuroma is an inflammation of the nerves in the foot that go to the toes. Although the name includes the word ?neuroma,? it is not really a tumor. It can affect any of the toes in the foot. However, it most often affects the nerves that run between the third and fourth, or second and third toes.
Morton's neuroma is an inflammation of the nerves in the foot that go to the toes. Although the name includes the word ?neuroma,? it is not really a tumor. It can affect any of the toes in the foot. However, it most often affects the nerves that run between the third and fourth, or second and third toes.





 Overview
Overview Symptoms
Symptoms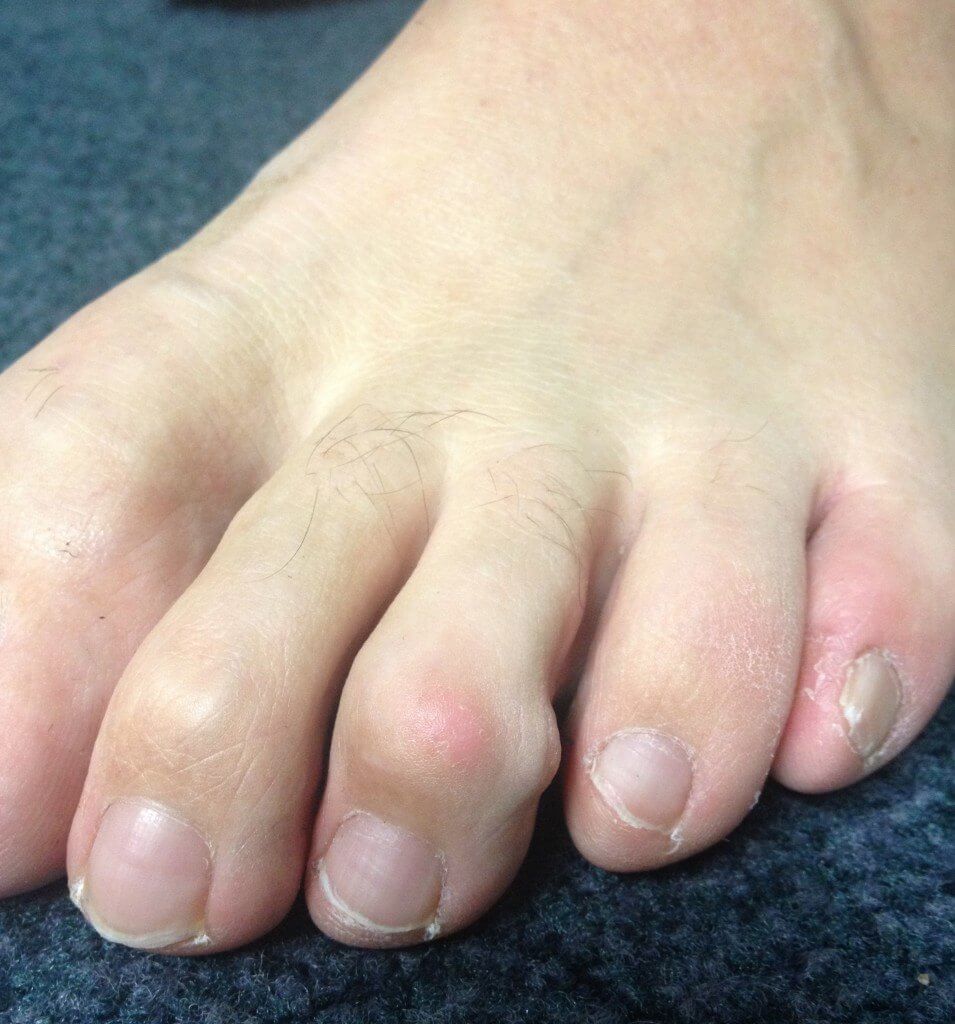 Prevention
Prevention